Smart Contract Development
A decentralised permissionless self-executing digital agreement with terms directly written into lines of code on a particular blockchain.
Trusted contributors in:
Why do we need smart contract?
Trustworthiness
Smart contracts automate and enforce agreements, ensuring all involved parties adhere to predefined terms without the need for intermediaries, which establishes a trustless environment.
Transparency & Immutability
Once deployed, smart contracts can't be altered, ensuring the terms remain constant. Moreover, their operations are visible on the blockchain, providing transparency for all parties.
Efficiency
By automating processes traditionally requiring intermediaries or manual management, smart contracts expedite transactions and lower associated costs.
Security
Leveraging blockchain's cryptographic foundation, smart contracts are protected from fraud and unauthorized alterations.
Cost Reduction
Eliminating intermediaries and streamlining operations, smart contracts reduce the fees and expenses linked to contract management and execution.
Accuracy
Automated execution reduces human errors commonly found in manual contract processing.
Global & Borderless
Smart contracts on public blockchains can operate across borders, facilitating international interactions without the need for central authorities or traditional banking systems
Programmability
Capable of integrating complex logic, smart contracts can accommodate dynamic and multifaceted agreements
Interoperability
They can seamlessly interact with other digital services, platforms, or smart contracts, creating interconnected ecosystems.
Censorship Resistance
Being decentralized, smart contracts are tough for any single entity to halt or manipulate, ensuring enforcement even in adversarial conditions
Our smart contracts development flow
01
Business logic and Requirements Definition
02
Token engineering and mathematical model
03
Architecture
04
Development and implementation
05
Unit tests and Deployment
06
Gas costs optimisation
07
Audit
Examples of using smart contracts
(module my-token G
(defcap G () true)
(defschema account
balance:decimal)
(deftable accounts:{account})
(defun create-account (acct:string)
(insert accounts acct {"balance": 0.0})
"Account created")
(defun credit (acct:string amount:decimal)
(update accounts acct {"balance": (+ (at 'balance (read accounts acct)) amount)})
"Balance credited")
(defun debit (acct:string amount:decimal)
(enforce (>= (at 'balance (read accounts acct)) amount) "Insufficient funds")
(update accounts acct {"balance": (- (at 'balance (read accounts acct)) amount)})
"Balance debited")
)
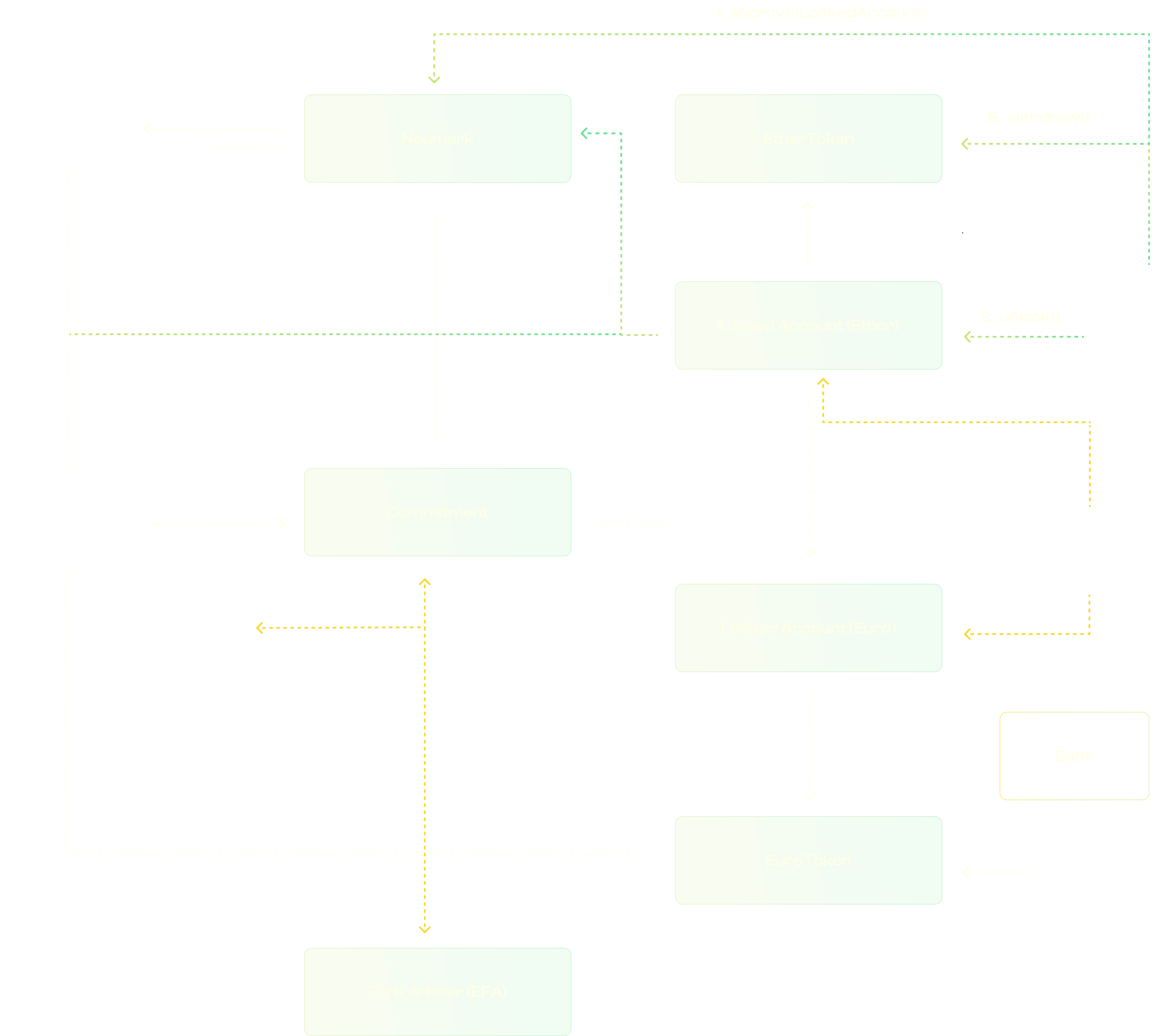
Smart contract architecture diagram sample
Smart Contract Tech Stack
Solidity
Vyper
Rust
Cairo
Move
Leo
JavaScript
Node.js
C/C++
Smart contract we built
Project description iLend is a decentralized finance protocol developed on the Injective network. It offers the ability to engage in lending and borrowing activities in a decentralized, transparent, and efficient manner. The protocol leverages Injective Protocol’s ability to offer fast, secure, and EVM-compatible DeFi transactions across multiple blockchain ecosystems. Project features 1. Basic borrow and…
Project description Deepwaters is the fusion of traditional finance and blockchain technology into a hybridarchitecture, leveraging proven concepts from both. Deepwaters aims to bring maturity to DeFi and enable systems that power the next generation of financial applications. Zpoken built Vault and lending contracts for DeepWaters, this solutions help to accumulate liquidity that powers trading…
Project description Dexilon is the first DEX that is run on a limit order book powered by the native blockchain. Democratically managed by the community in a trustless and verifiable way from the world’s leading brands. Core features making Dexilon unique and easy for users onboarding: Zpoken developed The development process for Dexilon exchange, a trailblazing…
